Commonly Used Materials of Plastic Bucket Mold
Plastic buckets are ubiquitous in our daily lives, serving a variety of purposes, from carrying liquids and foods to holding cleaning supplies and gardening tools. Behind the production of these versatile containers lies an essential component – the plastic bucket mold. The choice of materials for plastic bucket molds plays a crucial role in determining the mold's durability, functionality, and ability to produce high-quality buckets.
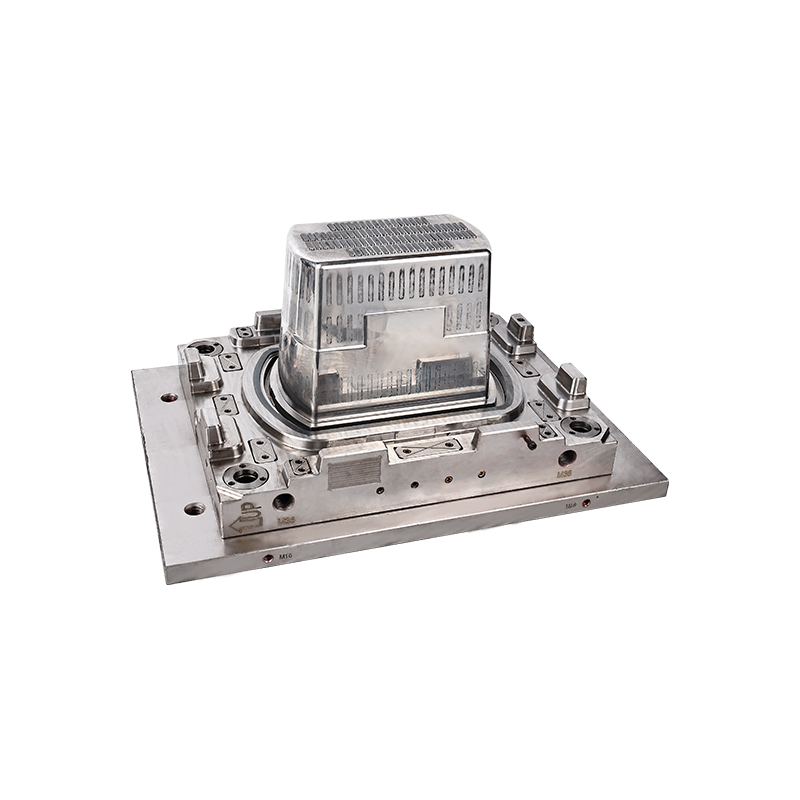
A plastic bucket mold is a specialized tool used in injection molding to create plastic buckets with specific shapes, sizes, and features. The mold consists of two halves, the cavity, and the core, which are precision-engineered to match the desired design of the plastic bucket. Molten plastic is injected into the mold, taking its shape as it cools and solidifies. Once the plastic is set, the mold is opened, and the finished bucket is ejected, ready for use.
The selection of materials for plastic bucket molds is critical for ensuring the mold's performance and longevity. The following materials are commonly used in the manufacturing of plastic bucket molds:
Steel: Steel is the most prevalent material for plastic bucket molds due to its durability and excellent thermal conductivity. Common types of steel used include:
P20: P20 is a low-carbon mold steel, often used for general-purpose molds. It offers good machinability and polishability, making it suitable for producing plastic buckets with smooth surfaces.
H13: H13 is a hot work tool steel known for its high resistance to heat and wear. It is ideal for molds used in high-volume production of plastic buckets.
S136: S136 stainless steel is corrosion-resistant and has good polishability. It is a popular choice for molds requiring a high level of surface finish.
Aluminum: Aluminum molds are becoming more popular due to their lightweight nature and faster cooling times. They are well-suited for lower volume production and prototyping applications. Aluminum molds are cost-effective and can be used for testing and initial production runs.
Beryllium-Copper: Beryllium-copper alloys offer excellent thermal conductivity, which aids in the cooling of the plastic during the molding process. These molds are often used for applications where fast cycle times are essential.
Pre-hardened Steels: Pre-hardened steels, such as Nak80 or 718, come with a hardness that requires minimal additional treatment. They offer good machinability and dimensional stability, making them suitable for producing intricate plastic bucket designs.
Impact of Material Choice on Mold Performance
The choice of material for the plastic bucket mold significantly affects the mold's performance and overall efficiency in the injection molding process:
Durability: Steel molds, such as P20 and H13, are known for their exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making them suitable for high-volume production.
Heat Transfer: The thermal conductivity of the mold material influences the cooling time of the plastic, affecting the overall cycle time and productivity. Materials like beryllium-copper and aluminum offer better heat transfer properties than standard steels.
Surface Finish: The material's polishability affects the surface finish of the plastic bucket. For a smooth and polished appearance, materials like S136 stainless steel are preferred.
Cost: The choice of mold material also impacts the overall cost of the manufacturing process. While steel molds may have higher initial costs, they offer longer lifespan and durability, reducing long-term expenses.
Proper maintenance of plastic bucket molds is essential for extending their lifespan and ensuring consistent performance. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection help prevent mold damage and maintain the quality of the plastic buckets.
The materials used in plastic bucket molds play a pivotal role in the production of high-quality plastic buckets. Steel remains the most commonly used material, offering durability, thermal conductivity, and polishability. However, aluminum and beryllium copper are gaining popularity for specific applications where faster cooling times and cost-effectiveness are crucial.

 English
English  русский
русский Español
Español






